Troubleshooting Network Bandwidth usage
a) dstat -f <==== Showed me that there is more network traffic on eth1 when compared to eth0 and that too.. it is outgoing traffic.
Dstat is a versatile replacement for vmstat, iostat and ifstat. Dstat overcomes some of the limitations of
these programs and adds some extra features.
Dstat allows you to view all of your network resources instantly, you can for example, compare disk usage in combination with interrupts from your IDE controller, or compare the network bandwidth numbers directly with the disk throughput (in the same interval).
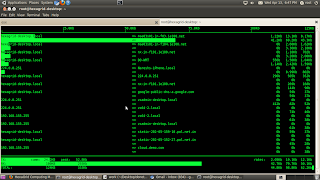
b) iftop -idisplays bandwidth usage information on an network interface
iftop does for network usage what top(1) does for CPU usage. It listens to network traffic on a named interface and displays a table of current bandwidth usage by pairs of hosts. Handy for answering the question
eth1 <==== Confirms what dstat says and also mentions which IP is pulling Data from public Server
c) nethogs eth1 <==== Shows which process is the culprit. apache2 is the process using up the bandwidth in sending job.
Net top tool grouping bandwidth per process
NetHogs is a small 'net top' tool. Instead of breaking the traffic down per protocol or per subnet, like most tools do, it groups bandwidth by process. NetHogs does not rely on a special kernel module to be loaded.
d) vnstat - good command to tell the usage.
vnStat is a network traffic monitor for Linux. It keeps a log of daily network traffic for the selected
interface(s). vnStat is not a packet sniffer. The traffic information is analyzed from the /proc filesystem, so vnStat can be used without root permissions.



No comments:
Post a Comment